The Centre will seek to convince states they should borrow from the market to meet the goods and services tax (GST) compensation cess shortfall, thus allowing the federal government room to raise funds in the event of hostilities with China escalating and allowing it to provide a stimulus to aid the Covid-hit economy.
States are well placed to raise funds from the market as their borrowings remain below the mandated level under the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act and have as much as ₹2 lakh crore parked in treasury bills, said officials with knowledge of the matter.
“We have to be more open to the idea of supporting the economy,” said a top government official, adding that the Centre is working on measures to lift the economy.
The Centre will compensate states fully for revenue loss on account of GST transition and revenue loss incurred due to Covid-induced slump and honour these commitments in “letter and spirit”, said a top government official.
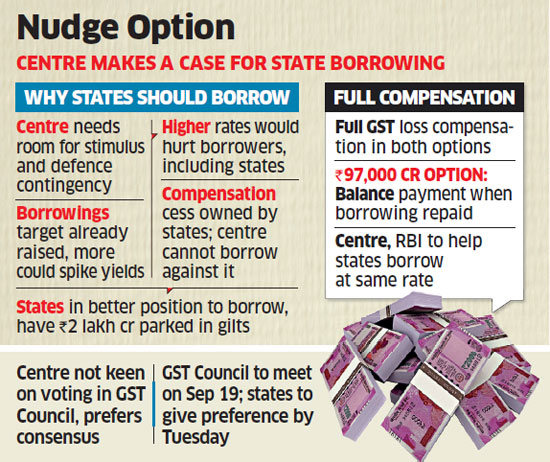
Even in the case of the first option, under which states will borrow ₹97,000 crore, they will not be denied the remaining amount.
Same Rate for All
“The remaining compensation will be paid to states after the above borrowing has been fully repaid,” said the official, adding that if the entire shortfall is borrowed, it will deny credit to the private sector, which is struggling to get back on its feet.
The debt window could be packaged in a way that it’s state independent altogether, to ensure all of them get the same rate, addressing the apprehensions of some that rates will be higher for them. The GST Council meeting scheduled for September 19 will take up the compensation issue again and states have to give their preference for the options offered by the Centre by today.
Who Should Borrow
On the issue of who should borrow, apart from the fact that states have more room, the official reasoned that the onus on borrowing rests with the states legally as well. The compensation cess is owned by the states. The Centre can borrow based on the security of its own taxes and resources, the Consolidated Fund of India, and not the compensation cess, which is owned by states, the person said.
Moreover, its view is that states are yet to exhaust their borrowing limit and have been provided additional room by the Centre under the Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) package.
The Centre will also facilitate funding arrangements along with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This will ensure states that want to borrow get the same rates that the Centre would, said the people cited above.
States have argued that the Centre should borrow the money and compensate them, opposing the two options that have been offered by it to them.
The Centre is keen to avoid voting at the GST Council on the proposals and maintain the practice of building a consensus. “We do not want it to be a vote… We want it to be through consensus,” another official said.
Two Options
The first of the two options offered by the Centre on August 26 entails borrowing of ₹97,000 crore, estimated as the revenue loss on account of GST transition, to be entirely serviced by cess collections. The second entails a borrowing of ₹2.35 lakh crore, the revenue loss estimated on account of GST transition as well as the Covid crisis.
Source : Times Of India
